🔄 Quick Recap
In Lesson 16, we discovered memory bottlenecks — the situations where even a fast CPU slows down because RAM can’t feed it data quickly enough.
So how do engineers solve this?
👉 By making memory pathways wider (multi-channel RAM) and smarter (low-power RAM for mobile).
This lesson is a double feature:
-
How multi-channel RAM increases speed.
-
Why low-power RAM (LPDDR) is essential for laptops, smartphones, and tablets.
By the end, you’ll see how both power and performance balance in modern memory design.
🛣️ Part 1: Multi-Channel Memory – More Lanes, More Speed
The Highway Analogy
Imagine a city highway. If it’s one lane, cars get stuck in traffic. If it’s two lanes (dual-channel), twice as many cars can travel at once. Four lanes (quad-channel) = even more throughput.
👉 Memory channels work exactly the same way.
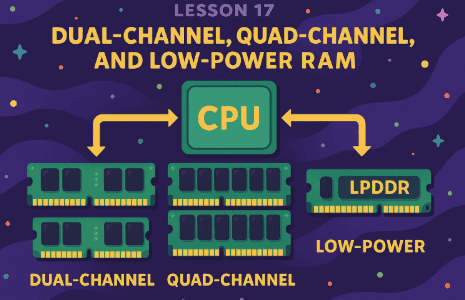
What is a Memory Channel?
A memory channel is the pathway between RAM and CPU.
-
Single-channel: One 64-bit wide path.
-
Dual-channel: Two 64-bit wide paths = 128-bit effective width.
-
Quad-channel: Four 64-bit wide paths = 256-bit width.
More width = more data per clock cycle.
📊 Bandwidth Example
Let’s calculate:
-
DDR4-3200 single-channel = ~25.6 GB/s bandwidth.
-
DDR4-3200 dual-channel = ~51.2 GB/s (double).
-
DDR4-3200 quad-channel = ~102.4 GB/s.
That’s the difference between loading a large game in 15 seconds vs 8 seconds, or a video render taking 30 minutes vs 20 minutes.
When Does Multi-Channel Matter?
-
Gaming: Dual-channel can increase FPS by 10–30% compared to single-channel.
-
Video editing & 3D rendering: Quad-channel speeds up file transfers and frame processing.
-
Servers: Often use 6-channel or 8-channel RAM to feed many cores simultaneously.
👉 But for light office use, dual vs single might not be noticeable.
NUMA vs Multi-Channel
Important distinction:
-
Multi-channel: Multiple parallel paths to the same memory.
-
NUMA: Multiple memory regions, each attached to different CPUs.
👉 Both solve bottlenecks, but in different ways.
Low-Power RAM (LPDDR) – Energy Efficient Memory for Mobile
Why Power Efficiency Matters
On desktops, speed is king. But in smartphones and laptops, power efficiency is just as important.
-
RAM uses electricity to refresh data constantly.
-
More power = shorter battery life.
-
Heat buildup is also a problem in thin devices.
This is why LPDDR (Low Power Double Data Rate RAM) was invented.
🧠 What is LPDDR?
-
Stands for Low Power DDR.
-
Used in smartphones, tablets, laptops.
-
Versions: LPDDR2 → LPDDR3 → LPDDR4 → LPDDR5 (current standard).
Each new generation improves speed + efficiency.
🔮 Future of RAM Configurations and Efficiency
-
LPDDR6 → will bring higher speeds for mobile gaming and AI apps.
-
Hybrid RAM → Combining high-bandwidth channels with low-power modes.
-
Unified Memory → Apple’s approach, where CPU and GPU share LPDDR, may become standard.